Page 37 - Market Analysis Report of Optical Communications Field in China & Global market 2020
P. 37
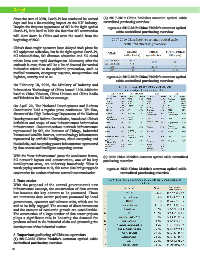
Figure 1: The number and permeability of 5G connections of 5G equipment suppliers. In addition, due to the recent
globally and in South Korea political actions of the United States against Huawei,
European countries such as the United Kingdom also
announced to abandon the use of Huawei equipment. The
spin-off of Huawei's equipment will also further slow 5G
progress in Europe.
U.S. carrier T-Mobile plans to deploy 5G in the 600MHz
band, while Sprint plans to deploy 5G in the 2.5ghz band.
Both companies' 5G bands are in the middle and low bands,
with good coverage. T-mobile and Sprint will combine
to create one of the broadest and highest-capacity mobile
networks in U.S. history, spending $30 billion over the next
three years to build new networks and deploy new services,
expecting to increase average speeds in the U.S. 15-fold by
2024.
2. Excluding China, global FTTH demand is still a
growth point in the market
Under the promotion of national broadband strategy,
mainstream operators in North America, Europe, Southeast
Asia, South Asia and other regions have been accelerating
fixed-line broadband scale construction. Indonesia's
National Broadband Plan and the Palapa project, for
example, are expected to increase fixed broadband
penetration to 13.4% by 2020; Indian telecom operator
Reliance Jio is pushing forward construction FTTH with
optical fiber base, and plans to provide FTTH service in
more than 1100 cities. Germany aims to have high-speed
will have launched 600,000 5G base stations, China Mobile
will add 250,000 new 5G base stations, and China Telecom Internet access for 99 percent of households, including
and China Unicom are expected to build more than 250,000 rural areas, by the end of 2021. Deutsche Telekom expects
new 5G base stations in 2020. In other words, the goal of to spend €2bn a year on all-fibre deployments in the future,
the three major carriers this year is to achieve 5G network adding 2m fibre broadband subscribers a year. Britain,
coverage in all cities and regions. No matter independent France, Italy and other major European countries have
networking or non-independent networking, 5G requires at also introduced national policies to accelerate FTTH
least 1.5-2 times as many outdoor macro stations as 4G. In construction.
2020, China will build more than 600,000 5G base stations, 3. Global 4G investment excluding China remained
and after 2021, it will form a scale of one million stations stable
per year. As deploying 5G, Telecom operators are still investing in
Figure 2: 5G CAPEX by China's three major operators in LTE network improvements, including carrier aggregation,
2020 4×4 MIMO, and VoLTE, LTE-A/LTE-A Pro. According to
statistics, 141 operators around the world will launch 4G
commercial networks from 2020, in addition, 64 operators
are investing heavily in VoLTE network and 37 operators
are investing heavily in LTE-A (LTE-Advanced) network.
Moreover, 159 operators worldwide are investing in nB-
Current Status of 5G in Europe and America iot networks, and 69 operators are investing in eMTC
2020 was supposed to be the start of the era of 5G networks. Therefore, although the construction of 4G base
infrastructure and spectrum allocation in the European stations in China has come to an end and is expected to
Union. But now, because of COVID-19 epidemic, EU decrease in 2020 compared with 2019, the investment in
countries' 5G plans have been put on hold. The EU's 4G in other global markets except China remains stable.
5G construction will lag behind China and other Asian
countries by at least a year or two, as the COVID-19 II: China Optical Communication Market
outbreak in Europe is likely to last longer than in Asia; and 1. Due to COVID-19 uncertainty, 5G will play a
there is no consensus among EU countries on the selection more prominent role as a new economic engine
37