Page 49 - Market Analysis Report of Optical Communications Field in China & Global market 2020
P. 49
of the fiber with a thermal barrier to reduce the effect of
(2-1) temperature on the fiber. The coating material of fiber
was developed by changing the polymerization state of
The parameters, the young's modulus (E ) and geometric the polymer material. Investigate the influence of fiber in
0
moment of inertia (I ) in the equation, are the axial force. extremely cold environment (-70 °C~-40 °C).
0
The mechanism of lateral forces ( ) is different, which
is the lateral contraction of the cladding layer and the 3.Experiment
superposition of the lateral stress between the intersections Combining with basic theory of the influence of the
of layers. The lateral force caused by the contraction of the additional attenuation of the fiber and the coating material
cladding layer is defined as shown in equation 2-2: above, and the conclusion of the experimental test, a new
type of ultra-cold-resistant & ultra-large capacity G.654.E
(2-2) fiber was developed. Meanwhile, attenuation characteristics
of the fiber in different extreme environments were studied
is the radius of the fiber in the equation. It is assumed that to make sure the parameters satisfied the requirements of
the deformation (W) caused by the lateral contraction of use in the environment of -70 °C.
the optical fiber shows the sine wave of spatial frequency:
The transmission characteristics of the optical fiber
(2-3) are basically independent of temperature, but since the
temperature has an influence on the stress of the optical
In the equation, is constant, which represents length, and fiber, there is a certain difference between the elongation of
its spatial frequency is unknown in the deformed optical the optical fiber coating layer and the bare optical fiber, and
fiber. We expressed this distortion as: the extension of the optical fiber is more or less determined
by the joint action of the both. Micro-bending is caused by
(2-4) fiber contraction when the temperature is very low, thereby
increasing the attenuation. In this paper, the attenuation
By applying the NTH term in equations (2-3) and (2-4), the characteristics of the fiber under extreme conditions are
initial deformation of the optical fiber can be obtained. investigated in detail by studying the attenuation variation
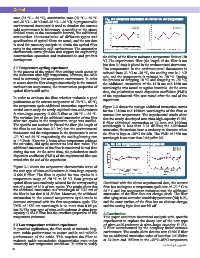
of the fiber in the temperature range of -70 °C to 85 °C.
(2-5)
Considering the temperature range of the fiber from -70
Since the research does not involve the cabling process, the °C to 85 °C, previous research experience on ordinary low
stress on the fiber is primarily determined by the coating temperature resistant communication fiber shows that the
material of the fiber and the interaction between the fiber fiber characteristics are basically unaffected at normal use
cladding and the core layer. Therefore, it is effective to temperature (-10 °C~40 °C). The effect of the temperature
considered two aspects above and explored ways to solve on the attenuation of the fiber means that the micro-bend
the problem to improve the low temperature performance has an effect on the attenuation of the fiber. In the range
of optical fiber. of -40 °C~-10 °C, the fiber temperature characteristics are
mainly low temperature additional attenuation, in the range
2.2 Coating Materials of 40 °C~85 °C, the fiber temperature characteristics are
The mechanism of optical fiber transmission attenuation mainly high temperature additional attenuation, as shown
with temperature is that the linear expansion coefficient of in Figure 2-1.
bare optical fiber materials does not match that of coated Fig.2-1 Fiber additional attenuation with temperature (-40~85 °C)
materials. The fiber has good transmission characteristics
and enough mechanical strength at normal temperature, but
at low temperature, the shrinkage of the coating layer may
be greatly different from the shrinkage of the bare fiber, and
the bare fiber is longitudinally strained by the longitudinal
pressure of the coating layer [2] . When the difference
exceeds the longitudinal bending limit, micro-bends occur
and additional attenuation occurs. When the temperature
is higher than normal temperature, the loosened bare fiber
produces a micro-bends phenomenon due to the stress of
the coating layer, resulting in additional attenuation.
Based on the above analysis, the research on low
temperature resistant fiber (≤-70 °C) should mainly
improve the glass transition temperature of the coating Through the study of the additional attenuation
layer and lower its melting point to reduce the difference characteristics of optical fiber: it can be divided into three
of linear expansion coefficient between the coating layer areas according to the variation range of attenuation:
and the bare fiber; It is also possible to cover the surface normal temperature zone (15 °C ~ 35 °C), micro-increasing
49